Your Cart is Empty
Free Shipping in the USA.
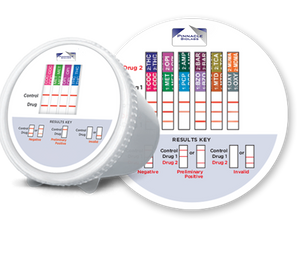
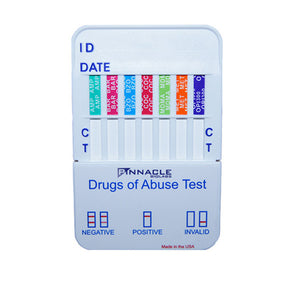
The Pinnacle BioLabs 12 Panel Drug Test is a rapid, point of care testing device that renders results, from urine, in one to three minutes. This dip device tests for the following drugs including 7 illicit and 5 prescription drugs: Marijuana | Cocaine | Amphetamines | Methamphetamines | Barbituates | Anti depressants | Oxycotin | Ecstasy | PCP | Methadone | Bupernorpine | Benzodiezopines

Amphetamines are central nervous stimulants whose effects include alertness, wakefulness, increased energy, reduced hunger and an overall feeling of well being. Large doses and long term usage can result in higher tolerance levels and dependence. The most common source for amphetamine are the prescription diet pills (Phentermine).
Methamphetamine is a stimulant drug which is quickly metabolized to amphetamine. It is used in pill form, or in powdered form by snorting or injecting. Crystallized methamphetamine is inhaled by smoking and is a considerably more powerful form of the drug. Some of the effects of methamphetamine use include: increased heart rate, wakefulness, physical activity and decreased appetite. Methamphetamine use can cause irreversible damage to the brain, producing strokes and convulsions, which can lead to death. Ecstasy, a new trendy and popular drug among teenagers is a refined and processed form of methamphetamine.
Opiates are any of the addictive narcotic drugs derived from the resin of the poppy plant. Opiates are analgesics (pain reducers) which work by depressing the central nervous system. They can also depress the respiratory system. Doctors often prescribe them for severe or chronic pain. Opiates are very addictive, both physically and psychologically. Use for only a short time normally results in addiction. Some commonly used opiates are: Codeine, Darvon, Heroin, Methadone, Morphine, Opium, Percodan, Talwin, Dilaudid and Demerol. Opiates are commonly referred to as "downers". Opiates can appear in many forms: white powder or crystals; small white, yellow or orange pills; large colorful capsules; clear liquid and dark brown, sticky bars or balls. Heroin accounts for the majority of the illicit opiate abuse. Some physical indications of opiate use include: extreme loss of appetite and weight, needle tracks or punctures, black and blue marks from "skin popping", scars along veins, cramps, nausea, vomiting, excessive scratching and complaint of itching, excessive sweating, constipation, raw, red nostrils from snorting, runny nose, pin-point pupils and watery eyes, reduced vision, drowsiness, euphoria, trance-like states, excessive thirst, tremors, twitching, unkempt appearance, strong body odor, irritability, chills; slight hallucinations and lethargy. Opiates reduce attention span, sensory and motor abilities, produce irrational behavior, depression, paranoia, and other psychological abnormalities.
Also classified as depressants, benzodiazepines are used therapeutically to produce sedation, induce sleep, relieve anxiety and muscle spasms and to prevent seizures. In general, benzodiazepines act as hypnotics in high doses, as anxiolytics in moderate doses and as sedatives in low doses. Like the barbiturates, benzodiazepines differ from one another in how fast they take effect and how long the effects last. Shorter acting benzodiazepines, used to manage insomnia, include estazolam (ProSom), flurazepam (Dalmane), quazepam (Doral), temazepam (Restoril) and triazolam (Halcion). Benzodiazepines with longer durations of action include alprazolam (Xanax), chlordiazepoxide (Librium), clorazepate (Tranxene), diazepam (Valium), halazepam (Paxipam), lorazepam (Ativan), oxazepam (Serax) and prazepam (Centrax). Abuse of Benzodiazepines occurs primarily because of the "high" which replicates alcohol intoxication. Approximately 50 percent of people entering treatment for narcotic or cocaine addiction also report abusing benzodiazepines.
Although chemically unlike morphine or heroin, methadone produces many of the same effects. Methadone is primarily used today for the treatment of narcotic addiction. The effects of methadone are longer-lasting than those of morphine-based drugs. Methadone's effects can last up to 24 hours, thereby permitting administration only once a day in heroin detoxification and maintenance programs. Ironically, methadone, used to control narcotic addiction, is a frequently abused narcotic, often encountered on the illicit market and methadone has been associated with a number of overdose deaths.
Tricyclic antidepressants have been prescribed since the 1950s for depression and compulsive disorders. Until recently TCAs were the primary choice of physicians for the vast majority of people with major depressive disorders. Ironically TCAs are often prescribed for symptomatic treatment of drug addiction and withdrawal and in particular, alcoholism. Tricyclic antidepressants work by raising the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain by slowing the rate of reuptake, or re-absorption, by nerve cells. Usually TCAs are taken over an extended period as results from the drugs are gradual. Because of the possibility of causing serious cardiac complications, TCAs can be lethal if misused at high doses. Abuse of TCAs can be the result of fear of relapse rather than any psycho-pharmacological effect however the potential for TCA abuse is well established, since the drugs have clearly defined euphoric psychological and stimulatory physiological action in cases of chronic usage. Generic and brand names of the tricyclic antidepressants include Adapin, Amitriptyline, Amoxapine, Asendin, Desipramine, Doxepin, Elavil, Imipramine, Ludiomil, Maprotiline, Norpramin, Nortriptyline, Pamelor, Pertofrane, Protriptyline, Sinequan, Surmontil, Tofranil, and Vivactil. Any comprehensive drug screening program should include a TCA panel.
Pharmaceutical drugs Percodan, Percocet, Roxicodone, Oxycontin. While classified as an Opiate, the chemical structure and metabolite of Oxycodone requires a separate Opiate test with a substantially higher sensitivity detection level than that of the standard Opiate drug test. Consequently, a positive test result will not only confirm Oxycodone but other opiates as well. In this regard the Oxycodone test is not Oxycodone specific but opiate specific being able to detect Oxycodone/opiate use at the higher sensitivity level required while the 2000 ng/ml sensitivity level of the standard opiate test would not detect Oxycodone. Oxycodone is generally prescribed in oral pill form with the analgesic buffer Acetaminophen. Acetaminophen, 4'-hydroxyacetanilide, is a non-opiate, non-salicylate analgesic and antipyretic which occurs as a white, odorless, crystalline powder, possessing a slightly bitter taste. Its molecular formula is C8H9NO2. The molecular weight is 151.17. The Oxycodone component is 14- hydroxydihydrocodeinone, a white, odorless, crystalline powder having a saline, bitter taste. It is derived from the opium alkaloid thebaine. Its molecular formula is C18H21NO4·HCl. The molecular weight is 351.83.
PPX is a narcotic analgesic compound bearing structural similarity to methadone. As an analgesic, propoxyphene can be from 50-75% as potent as oral codeine. DarvocetTM, one of the most common brand names for the drug, contains 50-100 mg of propoxyphene napsylate and 325-650 mg of acetaminophen. Peak plasma concentrations of propoxyphene are achieved from 1 to 2 hours post dose. In the case of overdose, propoxyphene blood concentrations can reach significantly higher levels. In humans, propoxyphene is metabolized by N-demethylation to yield norpropoxyphene. Norpropoxyphene has a longer half-life (30 to 36 hours) than parent propoxyphene (6 to 12 hours). The accumulation of norpropoxyphene seen with repeated doses may be largely responsible for resultant toxicity.
Tetrahydrocannibinol (THC) is an active component in marijuana. Marijuana, a hallucinogen, is commonly ingested by smoking, but it may also be eaten. Marijuana may impair learning and coordination abilities. Marijuana is most commonly the drug of choice among teenagers and young adults. The hallucinogenic effect of Marijuana can lead to irrational behavior, disorientation, and paranoia. Low concentrations of THC persists in urine at a detectable concentration for many days after smoking. Marijuana is the most common recreational drug of abuse.
Cocaine is made from coca leaves. Its effects include alertness, wakefulness, increased energy and an overall feeling of euphoria. Cocaine may be smoked, inhaled ("snorted") or injected. Cocaine can be a very addictive drug. Cocaine is metabolized by the body into the chemical compound Benzoylecgonine.
Classified generally as depressants, barbiturates produce a state of intoxication that is remarkably similar to alcohol intoxication. Symptoms include slurred speech, loss of motor coordination and impaired judgment. Depending on the dose, frequency, and duration of use, one can rapidly develop tolerance, physical dependence and psychological dependence on barbiturates. Barbiturate abusers prefer the short-acting and intermediate-acting barbiturates pentobarbital (Nembutal), secobarbital (Seconal) and amobarbital (Amytal). Other short-and intermediate-acting barbiturates are butalbital (Fiorinal, Fioricet), butabarbital (Butisol), talbutal (Lotusate) and aprobarbital (Alurate). After oral administration, the onset of action is from 15 to 40 minutes and the effects last up to 6 hours.
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (Ecstasy) is a designer drug first synthesized in 1913 by a German drug company for the treatment of obesity. Those who take the drug frequently report adverse effects, such as increased muscle tension and sweating. MDMA is not clearly a stimulant, although it has, in common with amphetamine drugs, a capacity to increase blood pressure and heart rate. MDMA does produce some perceptual changes in the form of increased sensitivity to light, difficulty in focusing, and blurred vision in some users. Its mechanism of action is thought to be via release of the neurotransmitter serotonin. MDMA may also release dopamine, although the general opinion is that this is a secondary effect of the drug. The most pervasive effect of MDMA, occurring in almost all people who have taken a reasonable dose of the drug, is to produce a clenching of the jaws. Symptomatic and biological responses to MDMA are similar to those produced by methamphetamine.
Phencyclidine hydrochloride (or PCP), also know as "angel dust," is a hallucinogen. PCP is commonly taken orally, by inhalation, by "snorting" or by injection. The effects of this drug are unpredictable and variable. Users may exhibit signs of euphoria, anxiety, relaxation, increased strength, time / space distortions, panic or hallucination. PCP use can lead to paranoia and extreme irrational behavior. Once popular, PCP use has declined dramatically in recent years and is no longer considered a major drug of abuse.